Ph.D. in Biomedical Engineering - Biomaterials & Tissue Engineering: Introduction, Admission, Registration, Eligibility, Duration, Fees, Syllabus 2024
Introduction:
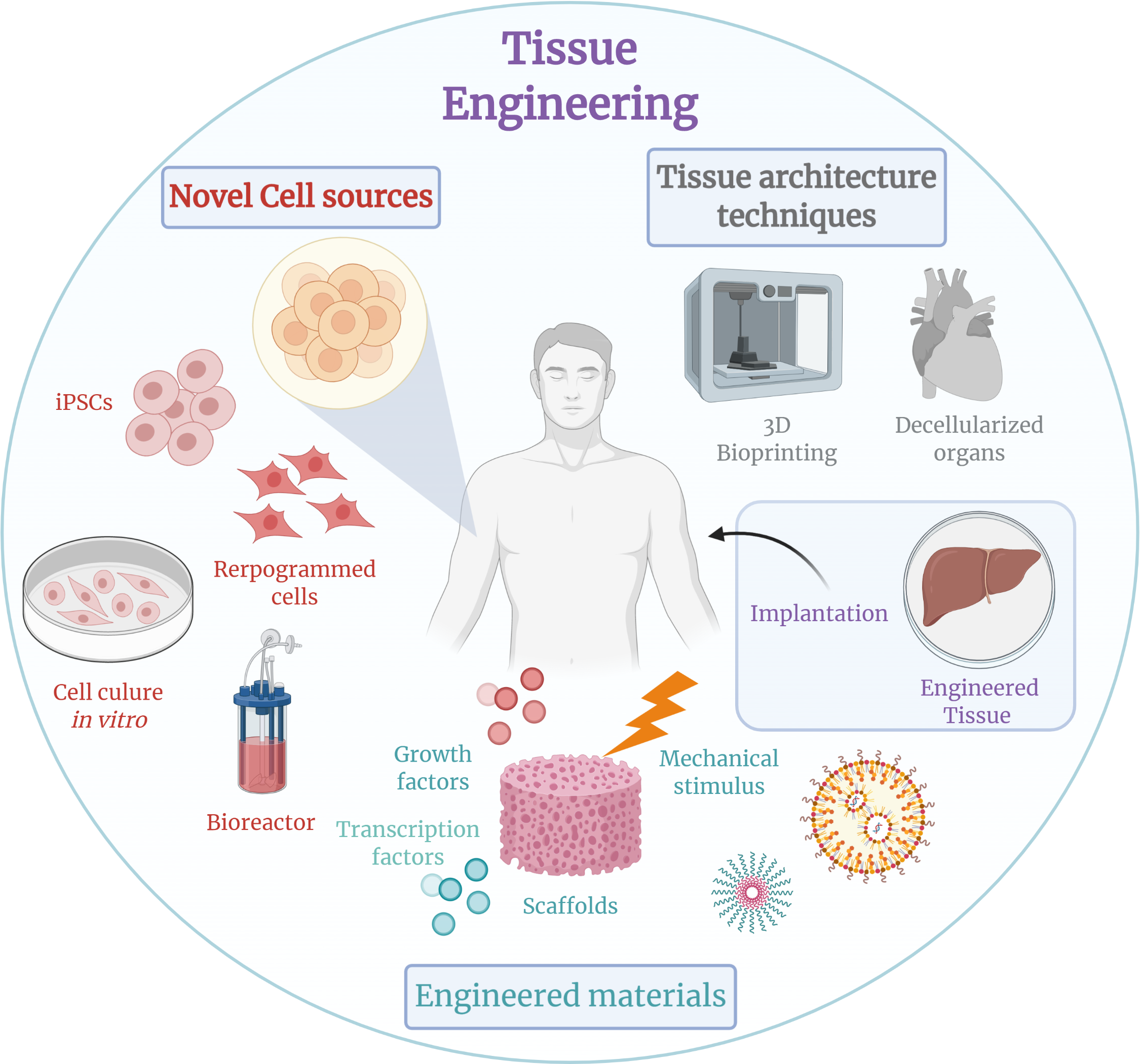
A Ph.D. in Biomedical Engineering is a pinnacle academic program that blends engineering principles with biological and medical sciences to advance healthcare. This degree prepares students to develop innovative technologies and solutions that improve patient care, from diagnostic tools to regenerative medicine. It’s a field where engineering ingenuity meets clinical needs, leading to transformative breakthroughs in medicine.
Admission Process:
- Submission of a comprehensive application including a statement of purpose.
- A strong academic record with a background in engineering or life sciences.
- Letters of recommendation from academic or professional mentors.
- A research proposal that aligns with the department’s expertise.
- An interview with faculty members.
- GRE scores, if required by the institution.
Eligibility:
- A Master’s degree in engineering, biology, or a related field.
- Research experience in a biomedical engineering context.
- Publications or conference presentations in related areas.
- A clear vision for research and its potential impact.
- Endorsement from a faculty member for doctoral supervision.
- Proficiency in relevant technical skills and software.
Completion Time:
A Ph.D. in Biomedical Engineering typically takes 4-6 years to complete. This period is dedicated to coursework, research, and the development of a dissertation that contributes novel insights or technologies to the field.
Career Opportunities:
- Research and development roles in medical device companies.
- Academic faculty positions in universities.
- Clinical engineer in healthcare facilities.
- Biotechnology entrepreneur.
- Consultant in biomedical engineering.
- Policy advisor in health technology.
Syllabus:
- Advanced biomaterials and tissue engineering.
- Biomechanics and mechanobiology.
- Medical imaging and bioinstrumentation.
- Computational biology and bioinformatics.
- Neural engineering and rehabilitation engineering.
- Regulatory affairs in biomedical engineering.
Internship Opportunities:
- Medical device and biotechnology companies.
- Research labs in hospitals and universities.
- Startups focused on healthcare innovation.
- Governmental health agencies.
- Non-profit organizations in global health.
- Clinical research organizations.
Scholarship and Grants:
- Teaching and research assistantships.
- Fellowships from scientific and engineering societies.
- Grants from national health institutes.
- Scholarships from university endowments.
- Industry-sponsored research projects.
- Travel awards for conferences and symposia.
FAQs:
What is Biomedical Engineering?
Biomedical Engineering is an interdisciplinary field that combines principles of engineering with biological sciences to develop technologies and systems that can improve healthcare.
What qualifications do I need to apply for a Ph.D. in Biomedical Engineering?
Typically, you need a bachelor’s or master’s degree in biomedical engineering or a related field. Strong academic records, research experience, and letters of recommendation are also important.
How long does it take to complete a Ph.D. in Biomedical Engineering?
The duration can vary, but it generally takes about 4-6 years to complete a Ph.D. program in this field.
What kind of research can I do during my Ph.D. in Biomedical Engineering?
Research areas can include medical imaging, biomaterials, biomechanics, tissue engineering, and more. It depends on your interests and the expertise available at your chosen institution.
Are there funding opportunities available for Ph.D. students in Biomedical Engineering?
Yes, many programs offer fellowships, research assistantships, and teaching assistantships that provide a stipend and tuition waiver.
Can I work while pursuing a Ph.D. in Biomedical Engineering?
While some students may work part-time, Ph.D. programs are demanding, and most students focus full-time on their studies and research.
